Application Lifecycle Management: Definition, Importance, and Process
The Application Lifecycle refers to the entire journey of a product or application—from its initial conception to its final requirements and eventual retirement. It represents the continuous process of evolution, where an application moves through different phases to deliver value over time.
These stages typically include:
- Ideation & Planning: Defining goals, scope, and resources.
- Design & Development: Building the architecture, writing code, and implementing features.
- Testing & Deployment: Validating functionality and releasing the application for use.
- Maintenance & Optimization: Updating, patching, and enhancing performance.
- Retirement or Replacement: Phasing out when it no longer serves business needs.
Understanding this lifecycle helps organizations align technology with business goals, maintain long-term sustainability, and continuously improve user experience.
Why is Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) Important?
ALM helps organizations stick to the requirements and release quality applications on time. It streamlines the entire lifecycle from ideation to delivery and makes sure that the product is thoroughly vetted and tested to meet the functional requirements as well as customer expectations.
But above all, it helps team members stay on the same page by improving communication, collaboration, and transparency.
There are a number of ALM solutions available in the market that help you monitor and track the lifecycle of the product from requirements gathering to deployment.
What is Application Lifecycle Management (ALM)?
Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) is the process of managing all stages of an application’s life. It integrates people, processes, and tools to ensure every phase—planning, design, development, deployment, maintenance, and retirement—runs efficiently and effectively.
Enterprise application lifecycle management software simplifies this process by providing automation, visibility, and collaboration tools. As a result, ALM has become the industry standard for delivering high-quality releases on time and within budget.
ALM Beyond Software Development
Although ALM is most commonly linked to software products, its approach and principles can be applied to any product development lifecycle.
For example:
- A bank uses ALM to deliver secure financial applications.
- A dairy farm applies ALM principles in managing supply-chain software.
- A retail chain relies on ALM-driven tools for e-commerce and logistics systems.
In today’s digital-first economy, every business depends on technology. That makes a well-defined ALM strategy essential for delivering seamless digital experiences.
ALM as Framework and Model
In practice, ALM can be understood as both:
- A framework that defines how applications are planned, built, and managed.
- An application lifecycle management model that guides organizations through every stage of software delivery.
This also involves application architecture models, which play a critical role in shaping how applications are structured, scaled, and evolved over time.
The principles remain the same across contexts, whether it’s:
- Agile ALM for startups
- Enterprise ALM for large corporations
Modern organizations increasingly adopt an integrated ALM approach, combining:
- Project Management
- DevOps practices
- IT Service Management (ITSM)
Disciplines Unified by ALM
Application Lifecycle Management integrates key business and technical disciplines to ensure applications meet requirements efficiently:
- Project Management – Aligning initiatives with business goals.
- Software Development – Building scalable, functional solutions.
- Quality Assurance (QA) – Maintaining performance and user satisfaction.
- IT Service Management (ITSM) – Ensuring reliable operations post-deployment.
For development teams, ALM provides:
- A framework for collaboration
- Tools for progress tracking
- Processes for quality assurance
- The ability to communicate more effectively across cross-functional teams
Together, these elements make ALM more than just a process—it becomes a strategic enabler for delivering reliable, high-quality applications. By aligning technology, people, and processes, organizations can accelerate innovation while keeping business goals at the center.
Phases of Application Lifecycle Management
Let’s take a look at the various phases of ALM and how they help in building a high-quality product, on time. The Phases of the ALM process—often described as distinct application lifecycle management steps in the ALM journey—start with defining application lifecycle management requirements and end with ongoing monitoring and retirement. This process flow ensures that each release aligns with business goals, compliance standards, and customer needs.
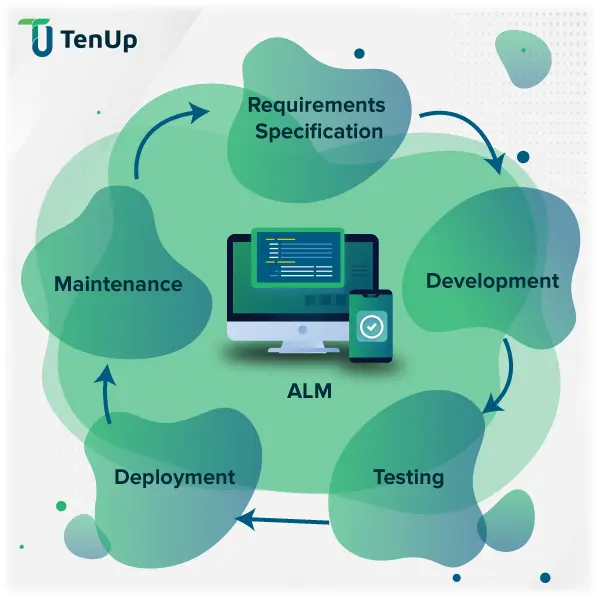
Requirements gathering
The first phase of the Application Lifecycle begins with requirements gathering and analysis. This is a very crucial phase because getting the requirements right is key to building the right product the first time. Multiple stakeholders have a role to play in defining the requirements scope to support their business case.
Requirements don’t just include business needs or feature specifications but also compliance and governance requirements.
There are multiple tools for requirements gathering used across industries such as IBM DOORS Next Generation, Modern Requirements, Jama Connect etc. Using tools to capture requirements helps maintain traceability and version control on the latest set of requirements.
Development phase
The product development commences when all the requirements have been finalised. At this stage, the project now moves from an idea to design and development. The development team breaks down the requirements specified into pieces and creates a phased development plan. There are many popular development approaches such as Waterfall model, Agile, or DevOps. Teams increasingly rely on modern practices like Feature flag strategies in Agile DevOps workflows to enable safer, faster iterations during the ALM process.
Based on the methodology, development teams and engineers use multiple tools to organize their tasks and manage the workflow effectively. For instance tools like Jira help manage the workflow and issues with its scrum and kanban boards and customized workflows.
Effective application lifecycle management is closely tied to the choice of application architecture, which influences how applications are developed and maintained throughout their lifecycle. To see how this connects with the phases of the ALM process, explore our detailed guide on evolving architecture models. Many application lifecycle management companies also recommend adopting application lifecycle management best practices to ensure this phase runs smoothly.
To explore how different architecture models have evolved to support modern development practices, check out our blog on Application Architecture Models and Their Evolution.
Testing and quality assurance
Without appropriate testing and quality assurance, there is no way to ascertain whether the development is on track and quality. Testers and Quality Assurance professionals verify that the application meets all the requirements that were specified at the outset. In addition, using a variety of testing approaches, the QA team also uncovers hard-to-predict scenarios and edge-cases that can lead to massive performance or software errors. Different types of tests are performed such as acceptance testing, integration testing, functional testing, performance testing, stress testing etc.
In the modern ALM context, QA is not an afterthought but almost a parallel activity alongside development to ensure that critical bugs are identified early in the lifecycle preventing expensive and risky product release delays. Strong application lifecycle management security and collaborative application lifecycle management practices also play a role in maintaining quality. Ideally, testers should be able to feed back on the application throughout the cycle.
The development and testing stages conclude once the application achieves a level of quality and stability that’s appropriate for release. Again, testers and QAs leverage best-of-breed test management and test automation tools to make the process more seamless and transparent.
Deployment
The deployment stage is when the product is finally deployed in production. The process varies based on the type of application that is being built, and choosing the right enterprise application lifecycle management software ensures that deployment strategies like blue-green and canary are implemented effectively. Typically, software as a service (SaaS) apps can be deployed on internal servers whereas web based apps are accessible through the internet.
Operations and maintenance
Just because a product has gone live, it doesn’t mean the lifecycle ends here. In the operations and maintenance phase, teams monitor and manage the application. In the DevOps world, this phase covers the “release” , “config” and “monitor” elements.
QA also plays a role here by finding and resolving bugs in the production environment. Finally, teams plan and prioritize the next updates to the product.
Choosing the Right Application Lifecycle Management Software
With the increasing complexity of applications, businesses need more than just processes—they need reliable application lifecycle management software to streamline workflows and ensure consistent delivery. The right Enterprise application lifecycle management software provides a unified environment for managing requirements, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance in one place.
When evaluating solutions, enterprises should consider:
- Scalability: Can the platform support large enterprise environments like those in banking, telecom, or healthcare where applications grow rapidly?
- Integration: Does it connect seamlessly with popular DevOps ecosystems such as GitHub, Jenkins, Kubernetes, or Docker? For many enterprises, DevOps unleashing ALM efficiency with cloud consulting provides the missing bridge between lifecycle management and scalable cloud-native delivery.
- Security & Compliance: Does it meet ISO 27001, GDPR, and HIPAA standards for regulated industries?
- Collaboration: Does it enable cross-functional teams—developers, QA engineers, and business analysts—to work together in real-time?
Gartner and Forrester frequently highlight vendors such as IBM Engineering Lifecycle Management, Micro Focus ALM, and Microsoft Azure DevOps as leaders in the ALM space. By implementing robust ALM software, organizations not only reduce development risks but also accelerate time-to-market while maintaining compliance and quality.
Top Application Lifecycle Management Tools for Modern Enterprises
Modern businesses rely on powerful application lifecycle management tools to manage the increasing demands of digital product delivery. These tools bring automation, visibility, and traceability into every stage of the application lifecycle.
Some widely adopted ALM tools include:
- Jira + Confluence (Atlassian) – Agile-friendly environment for requirements management, sprint tracking, and documentation.
- Micro Focus ALM / Quality Center – Popular in finance and insurance sectors where testing and compliance are critical.
- IBM Engineering Lifecycle Management (ELM) – Strong in aerospace and defense with requirements traceability and governance features.
- Azure DevOps (Microsoft) – A cloud-based platform widely adopted by enterprises shifting to CI/CD pipelines and hybrid cloud environments.
- ServiceNow Agile Development – Provides ITSM-driven ALM functionality, especially for IT operations teams in global enterprises.
- Polarion ALM (Siemens) – Known for supporting safety-critical industries like automotive, energy, and healthcare.
When deciding what are the top tools for managing application lifecycle management effectively, enterprises should also review analyst reports like the Gartner Magic Quadrant for Enterprise Agile Planning Tools or Forrester Wave for ALM Suites. These provide insights into vendor capabilities, innovation, and market leadership.
Benefits of Application Lifecycle Management (ALM)
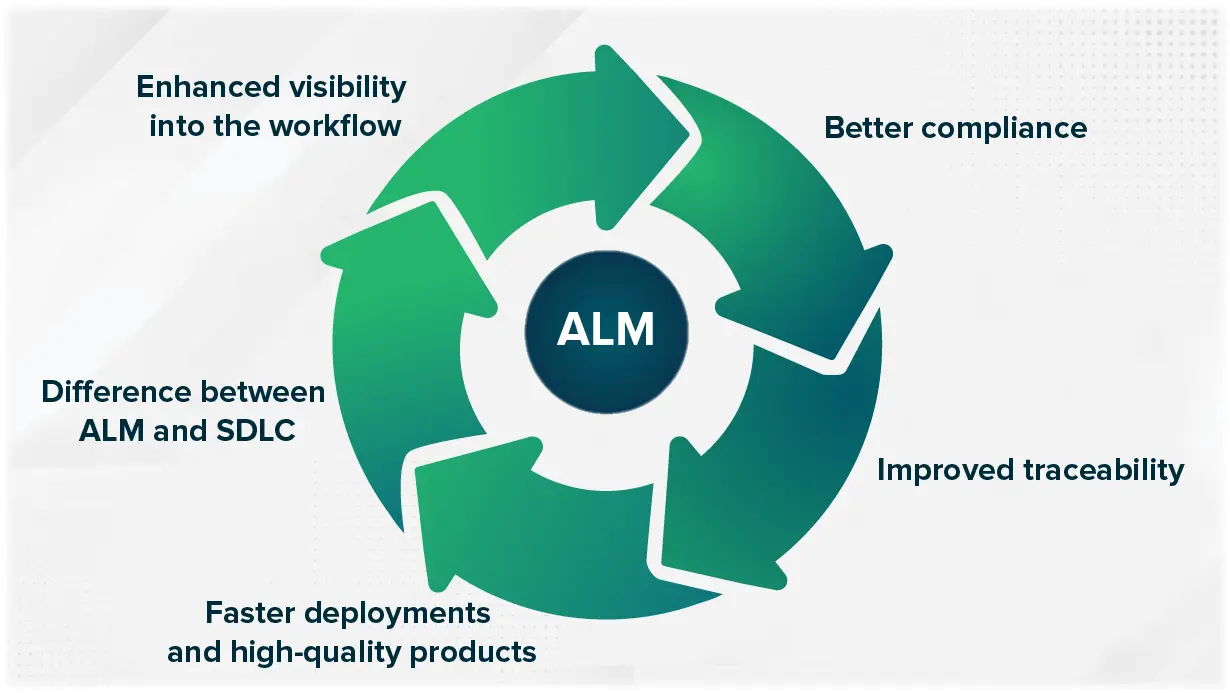
Enhanced visibility into the workflow
ALM helps enterprises to make more informed decisions regarding their application health. With application lifecycle management features such as real-time planning and version control, stakeholders can quickly map out the application’s future. ALM offers a clear direction for the workflow when the app is at the idea stage.
Better compliance
As applications are built on increasingly shorter timelines but in accordance with an evolving set of requirements and regulations, compliance is important. This is especially true in industries like pharma and healthcare, where healthcare application lifecycle management solutions are becoming essential. The healthcare application lifecycle management solution market has grown rapidly as organizations focus on meeting strict audit and regulatory needs. ALM offers better control over mapping compliance requirements to testing and coverage making it easier for regulated industries like pharma and healthcare to meet their audit goals.
Improved traceability
Are development and testing aligned to the defined requirements? How do you identify crucial gaps in test coverage? ALM solutions help establish virtual traceability between requirements, risks, tests and other activities. In fact, some of the modern tools enable e-Signature and other forms of virtual authentication necessary for defined milestones.
Faster deployments and high-quality products
With extensive visibility and collaboration across the project lifecycle, critical risks and defects are identified quickly and stakeholders can make better decisions. ALM not only offers a framework for software development but also helps you manage your application over time. The increased transparency and collaboration helps you release better quality products faster. For organizations modernizing their software lifecycle, cloud migration as an enabler for Agile and DevOps in ALM plays a critical role in making deployments more seamless and secure.
A 7-year study found that ALM adoption delivers tangible ROI—license and hardware costs were cut by a factor of 20, IT staff renewal effort reduced 30-fold, project launch times dropped from 3 months to just 3 hours, and compliance audit costs decreased by 4.5×.
Conclusion: Why Your Business Needs ALM Today
Managing the entire application lifecycle is key to making sure your software meets expectations and works efficiently from start to finish. Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) helps businesses ensure that all stages of development are well-organized, risks are managed, and quality is maintained. With ALM, you can bring together the right teams, track progress, and catch issues early before they become problems.
At TenUp, we understand how important ALM is for delivering a reliable, high-quality product. That’s why we offer complete application lifecycle management services, handling everything from planning and design to deployment and maintenance. This allows you to focus on growing your business while we take care of the technical details. Let us help you meet your product goals with the right approach to ALM.
Contact us today to learn more about how we can support your product strategy and development needs.
Frequently asked questions
Why should a growing company invest in ALM instead of basic project tools?
Basic project tools only manage tasks, while ALM connects strategy, development, testing, deployment, and compliance into one unified workflow. For a growing company, this means fewer silos, faster delivery, stronger quality control, and scalable governance, ensuring long-term efficiency that simple tools can’t provide.
How does ALM help reduce the time it takes to release new features?
ALM speeds up feature releases by combining Agile workflows with CI/CD automation, which means testing, approvals, and deployments happen faster and with fewer errors. By catching bugs early and keeping all teams aligned in one platform, it shortens release cycles while improving quality.
Is ALM too complex or expensive for startups and mid-sized businesses?
Not really. Today’s ALM platforms are designed to be lightweight, modular, and cloud-based. Startups don’t need to buy enterprise-level solutions upfront. They can begin with affordable tools for CI/CD, automated testing, or code management and scale as the business grows. This pay-as-you-grow model keeps costs predictable while removing the complexity barrier.
Can ALM work with cloud-based apps and legacy systems at the same time?
Yes. Modern ALM platforms are designed to manage both cloud-native applications and legacy on-premise systems in a single workflow. They offer integration with CI/CD, testing, and monitoring tools while supporting hybrid environments. This allows organizations to transition from legacy to cloud at their own pace, ensuring security, compatibility, and full lifecycle visibility across both systems.
What is the ROI of adopting ALM for enterprises?
Enterprises using ALM achieve up to 30% cost savings in the first year, faster release cycles (up to 50% quicker time-to-market), reduced defect rates, and stronger compliance readiness, delivering both immediate cost reduction and long-term productivity gains.
What’s the difference between ALM software and generic project management tools?
ALM software is purpose-built for managing the entire lifecycle of applications, from requirements and coding to testing, deployment, and updates. In contrast, project management tools focus on tasks, schedules, and resources across any type of project.
Can ALM be customized for regulated industries like fintech or healthcare?
Yes. Modern ALM platforms include compliance-ready workflows, audit trails, and traceability tailored to strict standards like HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and ISO. Many also provide industry-specific templates and integrate with regulatory frameworks, making them ideal for fintech and healthcare environments.
How does cloud-native development change the way ALM is implemented?
Cloud-native development modernizes ALM by replacing monoliths with microservices, automating CI/CD pipelines, and using containers with orchestration tools like Kubernetes. This makes ALM more agile, scalable, and resilient, enabling faster delivery, lower costs, and continuous innovation.

